Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer

Nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC) can be divided into two forms of carcinoma: (1) a basal carcinoma (BCC), which accounts for 75% of cases, and is a slow-growing, locally invasive tumour or (2) a cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), which accounts for the remainder of cases of NMSC (Samarasinghe, 2012). Compared to BCC, SCC has a significant rate of metastasis (Samarasinghe, 2012).
Morton’s Neuroma

Morton’s Neuroma is neuropathic pain in the forefoot and is related to the interdigital nerve (Gougoulias, 2019). It commonly occurs between the second and third metatarsals (Zabaglo, 2020). It is associated with pressure distribution changes in the foot due to either a deformity or calf muscle tightness (Gougoulias, 2019).
Morton’s Neuroma
Morton’s Neuroma is neuropathic pain in the forefoot and is related to the interdigital nerve (Gougoulias, 2019). It commonly occurs between the second and third metatarsals (Zabaglo, 2020). It is associated with pressure distribution changes in the foot due to either a deformity or calf muscle tightness (Gougoulias, 2019).
Cerebral Aneurysm

Cerebral aneurysms are vascular abnormalities in which a bulge in an artery in or near the brain is formed when the arterial walls are weak. The dilation of the aneurysm may vary in size, ranging from less than 0.5mm to greater than 25mm. Unruptured cerebral aneurysms are often asymptomatic and found incidentally upon neuroimaging or autopsy (Jersey, 2020). On a global scale, the prevalence of cerebral aneurysms is approximately 3.2%. The mean age of patients is 50 years old and there is a 1:1 gender ratio. However, the ratio is approaching 2:1 with increasing female predominance over the age of 50 (Jersey, 2020).
Cerebral Aneurysm

Author: Anushka Pradhan Editor: Heia Mansouri Dana Overview Cerebral aneurysms are vascular abnormalities in which a bulge in an artery in or near the brain is formed when the arterial walls are weak (Jersey, 2020). The dilation of the aneurysm may vary in size, ranging from less than 0.5mm to greater than 25mm (Jersey, […]
Intestinal Bowel Obstruction

Intestinal obstruction can be a mechanical or functional obstruction which can be found in either the small or large intestine (Smith, Kashyap, & Nehring, 2020). They account for 15% of hospital admission for acute abdominal pain in the USA (Catena et al., 2019), Small intestinal obstructions are more common (Schick, Kashyap, & Meseeha, 2020) while large intestinal abstractions account only for 10-15% of all intestinal obstructions (Smith, Kashyap & Nehring, 2020). Obstruction occurs when the lumen of the bowel becomes partially or completely blocked (Smith et al., 2020). This prevents the normal movement of chyme through the digestive system and can be a cause of morbidity and mortality (Catena et al., 2019).
Intestinal Bowel Obstruction
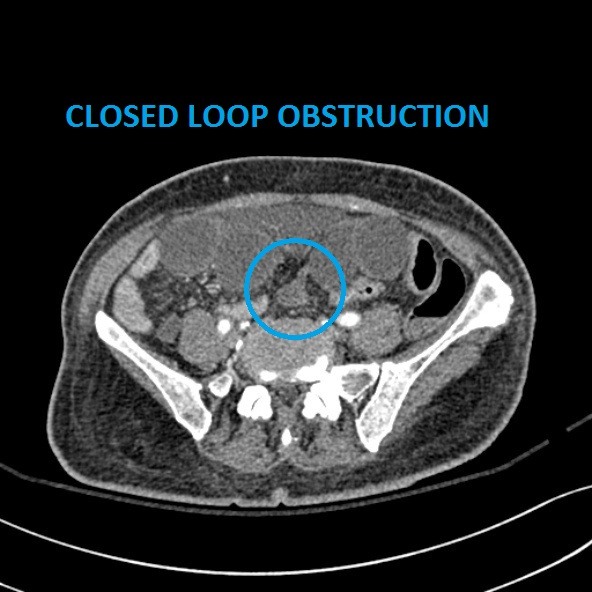
Intestinal obstruction can be a mechanical or functional obstruction which can be found in either the small or large intestine (Smith, Kashyap, & Nehring, 2020). They account for 15% of hospital admission for acute abdominal pain in the USA (Catena et al., 2019), Small intestinal obstructions are more common (Schick, Kashyap, & Meseeha, 2020) while large intestinal abstractions account only for 10-15% of all intestinal obstructions (Smith, Kashyap & Nehring, 2020). Obstruction occurs when the lumen of the bowel becomes partially or completely blocked (Smith et al., 2020). This prevents the normal movement of chyme through the digestive system and can be a cause of morbidity and mortality (Catena et al., 2019).
Acne
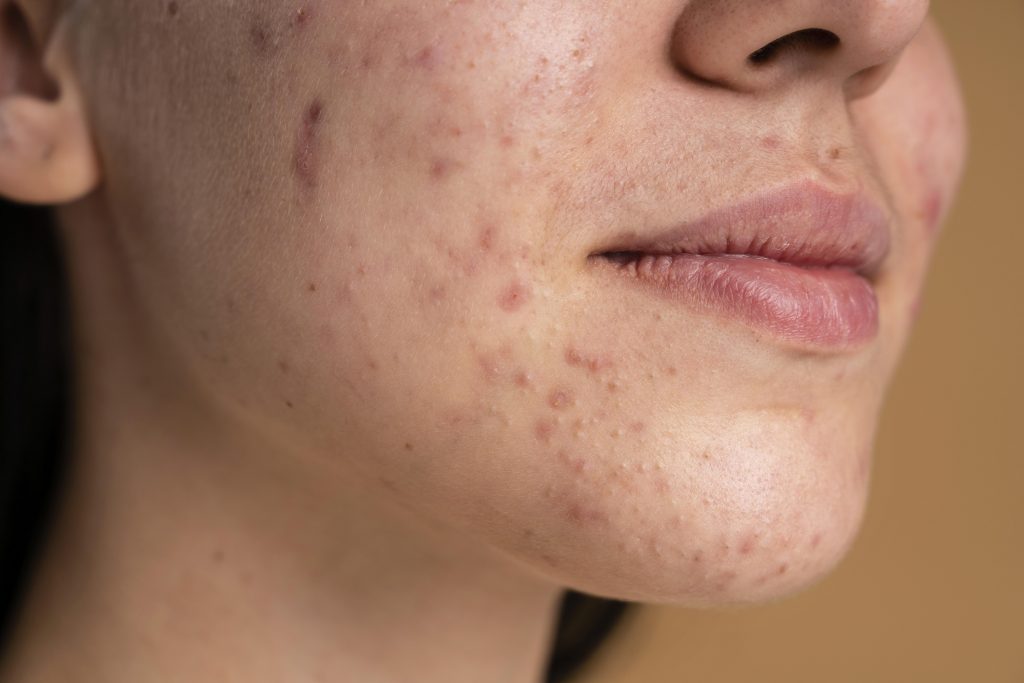
Author: Anushka Pradhan Editor: Daisy Li Overview Acne is a chronic inflammatory disease of pilosebaceous units which consist of the sebaceous gland, hair follicle and shaft (Kraft, 2011). It is most likely to occur in areas with high concentrations of sebaceous glands such as the face, back, and chest (Titus, 2012). It consists of characterized […]
Acne
Acne is a chronic inflammatory disease of pilosebaceous units which consist of the sebaceous gland, hair follicle and shaft. It is most likely to occur in areas with high concentrations of sebaceous glands such as the face, back, and chest (Titus, 2012). It consists of characterized lesions that lead to scarring and pigmentary changes which impact quality of life by decreasing self-esteem and hindering psychosocial development (Kraft, 2011).
